Percutaneous biportal endoscopic surgery was a minimally invasive approach and used two portals or two channels during operation. This approach is very similar to shoulder extra-cavitary arthroscopic surgery and percutaneous interlaminar endoscopic approach. One portal was used for endoscopy, and the other portal was used for working channel (Fig. 20.2).
Spinal instruments were used through working portal. Two portals should be joined around working area such as lamina or foramen. For the prevention of muscle injury, two portals should be made through loose epi-periosteal plane and inter-fascicular area (Fig. 20.3a). We have to make working space between muscle and bony structure (spinous process, lamina,
and facet joint) for initiation of biportal endoscopic approach (Fig. 20.3b). Continuous irrigation fluid helps to make and maintain working space. As operation proceeded, extra-cavitary procedure was converted to cavitary procedure (intraspinal canal, Fig. 20.3c). The view of operation field was getting cleaner as operation proceeded. Continuous irrigation system must be used for clearing of surgical field and bleeding control. Irrigation fluid was drained from endoscopic portal to working portal (Fig. 20.4). For the maintenance of pressure of irrigation fluid, irrigation fluid bag should be placed at about 170 cm height or used with irrigation pump system. Recommendation pressure of irrigation saline was 30–50 mmHg (height pressure control:
170 cm). Irrigation fluid should be continuously drained well via working channel during operation. If irrigation saline was not drained continuously, we checked patency of working portal and used a retractor for retraction of muscle and fascia.
We can use general spinal operation instruments such as Kerrison punches, pituitary forceps, hooks, and dissectors as well as endoscopic specialized instruments via working portal.
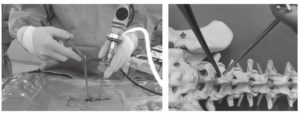
Fig. 20.2 Overview of percutaneous biportal endoscopic
surgery
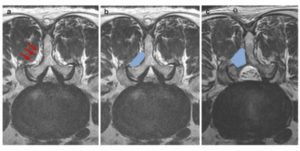
Fig. 20.3 Two channels were made via inter-fascicular area and epi-periosteal plane (a). Initial working space between
lamina and muscle (b). Working space was increased and vision was clearer after laminotomy (c)